What is HDL Cholesterol?
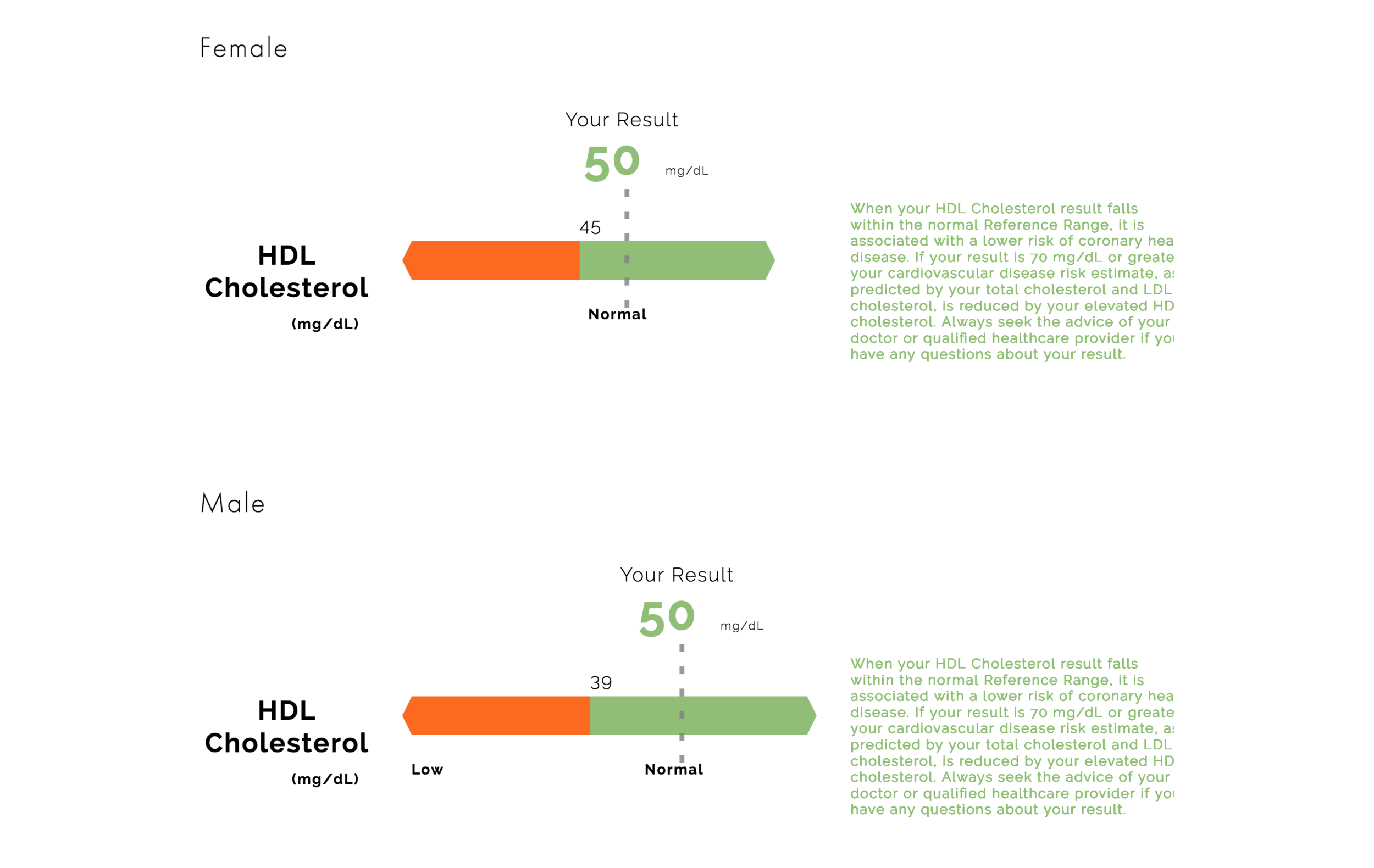
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, commonly called “good cholesterol,” is associated with a decreased risk of heart disease, and many doctors use HDL cholesterol levels to predict lifetime risk of a heart attack or stroke. HDL cholesterol also works to remove LDL cholesterol (or “bad” cholesterol) from the arteries by transporting it to the to the liver, where it can be broken down.
How to Measure Your HDL Cholesterol Level
In biometric screening results, HDL cholesterol will be measured in milligrams per deciliter of blood (mg/dL). A healthy level of HDL cholesterol for males is greater than 40 mg/dL, while a healthy level for females is greater than 46 mg/dL.
HDL Cholesterol and Nutrition
To increase HDL cholesterol or keep it in a healthy range, you should follow a healthy diet, eliminate tobacco exposure, and avoid excessive drinking. Additionally, there is a strong correlation between regular exercise and high HDL cholesterol levels. The ideal level of exercise to increase HDL cholesterol levels is moderate-intensity activity 3 to 5 times per week (the equivalent of burning about 1,200 to 1,600 kcal weekly).
Source: Quest Diagnostics Health & Wellness